
Sensors are the communication managers of automated industrial systems. They collect information about the environment and convert this information into a format that can be used by the system. Sensor selection depends upon what information the automated system needs to acquire.
Estimated completion time (hours): 1.4
Objectives
By the end of this course, you will be able to do the following:
- Define sensors
- List the primary types of sensors
- Categorize sensors based upon their capabilities
- Understand the role of sensors in automated industrial systems
- List some typical applications of sensors in automated industrial systems
Learning Path
- Maintenance Technician 3
Estimated Time (Hrs): 1.4
Language: English

Sensors have several properties and characteristics that affect their ability to detect and measure the environment and convert this information into a quantitative measurement. Understanding these characteristics will help you select the correct sensor for your application.
Estimated completion time (hours): 1.2
Objectives
By the end of this course, you will be able to do the following:
- Identify the characteristics of a sensor
- Explain how each characteristic impacts sensor performance
- Describe the criteria to be considered for selecting a sensor
Learning Path
- Maintenance Technician 3
Estimated Time (Hrs): 1.2
Language: English

Proximity sensors are typically designed to determine if an object is near and to communicate that information to another device in an automated system. Some proximity sensors simply detect if an object is present or absent, while others can measure the distance to the object. Other proximity sensors can even detect the color of an object.
Estimated completion time (hours): 1.4
Objectives
By the end of this course, you will be able to do the following:
- Understand proximity sensors
- Identify the different types of proximity sensors
- Understand the function of proximity sensors
- List some typical applications of proximity sensors
- Understand the symbology for proximity sensors
Learning Path
- Maintenance Technician 3
Estimated Time (Hrs): 1.4
Language: English
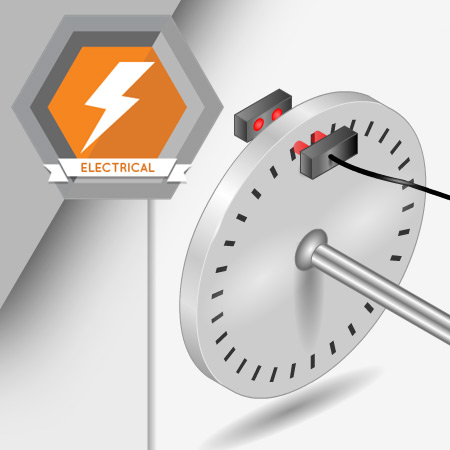
Position, speed, and acceleration sensors make it possible to move automated system components in complex ways. Controlling speed, position, and acceleration increases the efficiency of these systems as well.
Estimated completion time (hours): 1.7
Objectives
By the end of this course, you will be able to do the following:
- Identify the types of position sensors
- Understand the functions and features of position sensors
- Identify the types of speed sensors
- Understand the functions and features of speed sensors
- Identify the types of acceleration sensors
- Understand the functions of features of acceleration sensors
- Recognize some typical applications of position, speed, and acceleration sensors
Learning Path
- Maintenance Technician 3
Estimated Time (Hrs): 1.7
Language: English
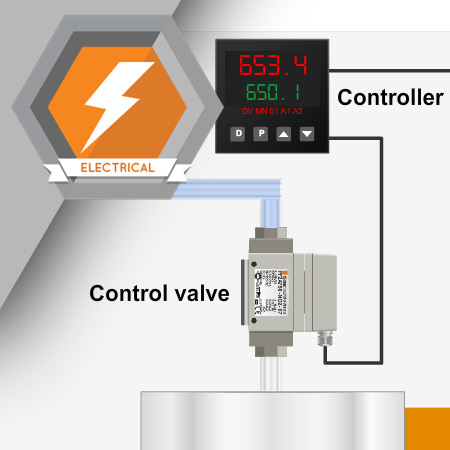
Industrial process sensors are designed to monitor conditions of a process that are variable, such as pressure, temperature, level, and flow. These sensors enable an automated system to control complex tasks, such as mixing, filling, heating, and cooling.
Estimated completion time (hours): 1.6
Objectives
By the end of this course, you will able to
- Describe the different types of process control sensors
- Describe common applications of process control sensors
- Differentiate between mechanical and electromechanical sensors
- Understand how a strain gauge functions
- Maintenance Technician 3
Estimated Time (Hrs): 1.6
Language: English

Many of the sensors you encounter in everyday life, such as barcode readers at retail stores, are also used in industrial processes. Understanding the uses of these advanced sensors is important for individuals working in these industries.
Estimated completion time (hours): 1.6
Objectives
By the end of this course, you will be able to do the following:
- Identify different types of advanced sensors used in industrial applications
- Describe the uses of barcode readers
- Define the main components of a barcode reader
- Describe the uses and types of radio frequency identification
- Describe the uses and types of vision sensors
- Describe the uses and types of laser sensors
- Identify typical applications of some advanced sensors
Learning Path
- Maintenance Technician 3
Estimated Time (Hrs): 1.6
Language: English
