
Critical thinking is one of many ways to think about information, problems you need to solve, or decisions you need to make. This course introduces you to critical thinking skills and how you might use them.
Estimated completion time (hours): 1.2
Objectives
By the end of this course, you will be able to do the following:
- Define critical thinking
- Describe how critical thinking relates to intuitive thinking
- Describe some examples of critical thinking skills
- List qualities shared by critical thinkers
- List intellectual values embraced by critical thinkers
- Explain some benefits of critical thinking
- List some barriers to critical thinking
Estimated Time (Hrs): 1.2
Language: English
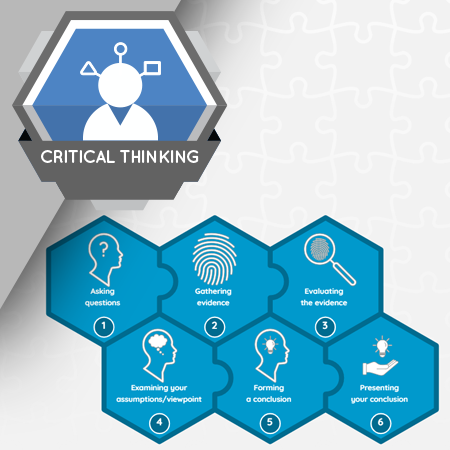
It’s human nature to make quick judgements and fast decisions, but fast decisions are not always the best decisions. The critical thinking process encourages you to slow down, define the problem or question you are considering, and examine various viewpoints. Taking a systematic approach can help you make better decisions.
Estimated completion time (hours): 1.5
Objectives
By the end of this course, you will be able to do the following:
- List the steps in the critical thinking process
- Describe qualities of good questions
- Define several different intellectual values
- List examples of research methods used to gather evidence
- Define the terms qualitative evidence and quantitative evidence
- Define the terms primary source and secondary source
- Describe methods for evaluating evidence
- Explain the difference between facts and opinions
- Define the terms assumption and inference
- Explain the importance of considering other points of view
- Describe what happens after you form a conclusion
Estimated Time (Hrs): 1.5
Language: English
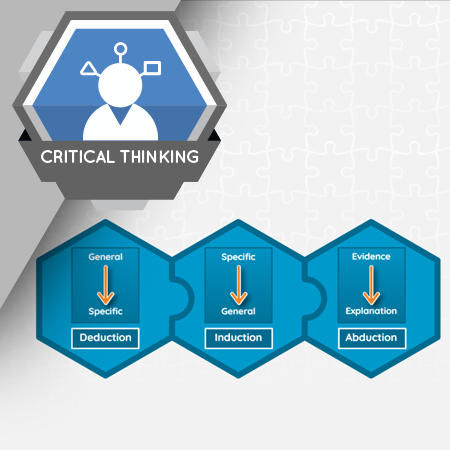
Understanding arguments and how they are constructed makes it easier to analyze another person’s point of view and decide whether you agree with it. Understanding arguments also helps you construct your own arguments and be more persuasive.
Estimated completion time (hours): 1.4
Objectives
By the end of this course, you will be able to do the following:
- Explain the structure of an argument
- Define the terms premise and conclusion
- Define signal words
- Identify the premises and conclusion in an argument
- List signal words for premises and conclusions
- Describe the differences between deductive, inductive, and abductive reasoning
- Explain how the terms valid and sound relate to deductive arguments
- Explain how the terms strong and cogent relate to inductive arguments
- Define the term logical fallacy
- Describe several examples of logical fallacies
- Define the term counterargument
Estimated Time (Hrs): 1.4
Language: English
