
Fiber based composites are often referred to as advanced composites. Understanding the forms in which fiber is made is important information for anyone working with fiber reinforced composites.
Estimated completion time (hours): 0.9
Objectives
By the end of this course, you will be able to do the following:
- Identify common fiber materials used in advanced composites
- Define tow
- Define yarn
- Define filament
- Identify common forms made of fibers

There are many different applications for fibers, tapes, and fabrics in the manufacture of composite parts. Understanding the properties of each form of composite material is important information for anyone working with composite materials.
Estimated completion time (hours): 1.1
Objectives
By the end of this course, you will be able to do the following:
- Understand how plies of tape can strengthen a composite part in multiple directions
- Identify common fabric weaves
- Define fabric drapability and symmetry
- Identify how the fabric weaves effect fabric properties

The two most common materials used in fiber reinforced plastics are glass and carbon. Understanding the properties of these two fiber materials is important information for anyone working with fiber reinforced composites.
Estimated completion time (hours): 1.2
Objectives
By the end of this course, you will be able to do the following:
- Define terms including tensile strength, stress, elastic range, plastic range, strain, tensile modulus, shear or rigidity modulus, and brittleness
- Describe the properties of e-glass and s-glass
- Identify the steps in the manufacturing process of glass fibers
- Describe the properties of carbon fibers
- Identify the steps in the manufacturing process of carbon fibers
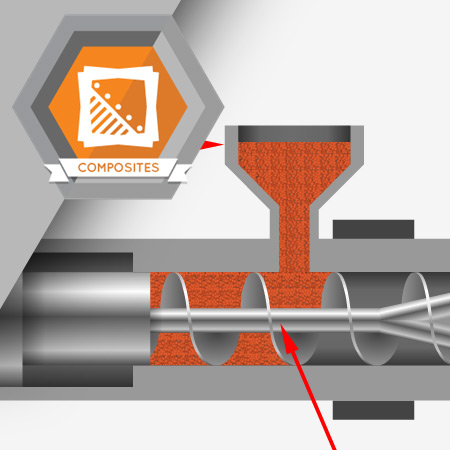
The matrix is an important constituent of fiber reinforced plastics. Understanding the types and properties of matrices is important information for anyone working with fiber reinforced plastics.
Estimated completion time (hours): 1.3
Objective
By the end of this course, you will be able to do the following:
- Define a polymer, monomer, and mer
- Define resin
- Define hydrocarbon
- List different polymers used as matrices
- Differentiate between thermoset and thermoplastic materials
- Define the advantages of prepreg and two-part resin systems

The curing process is a critical step in the production of a composite part. Understanding the curing process is important information for anyone working with composites.
Estimated completion time (hours): 1.1
Objectives
By the end of this course, you will be able to do the following:
- Understand the importance of the curing process in the production of composite parts
- Define ramp rate and soak/cure time
- Understand the importance of ramp rates and soak/cure times
- Understand the difference between atmospheric, gauge, and vacuum pressure
- Distinguish between co-curing and co-bonding
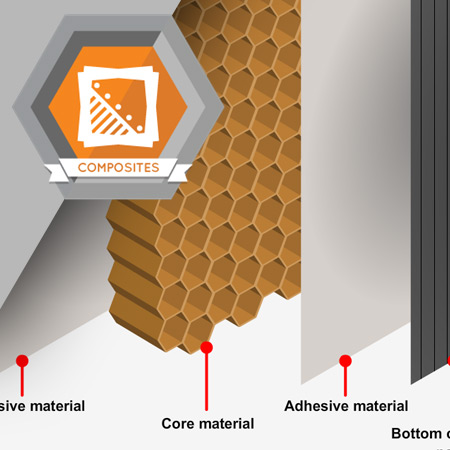
Honeycomb core materials are used in sandwich structures. A sandwich structure is a structure that has two composite skin bonded to a core material.
Estimated completion time (hours): 0.9
Objectives
By the end of this course, you will be able to do the following:
- Define the three stresses that interact with a honeycomb core structure
- Explain how these stresses are reduced through the use of honeycomb core materials
- List the most common types of honeycomb core materials
- Describe and differentiate between the honeycomb core materials
- List the three honeycomb core cell shapes
- Explain how honeycomb core materials are used in commercial applications
- Describe the four types of edge sealing
- List the tools that are used to cut and finish honeycomb core materials
Describe the purpose of adhesive film in a honeycomb structure

A sandwich structure is a structure that has two composite skin panels adhesively bonded to a core material. When different materials are used together, they must be compatible.
Estimated completion time (hours): 0.7
Objectives
By the end of this course, you will be able to do the following:
- Define sandwich structures
Explain the compatibility between carbon fiber and expanded paper, aramid, aluminum, and foam core

Galvanic corrosion occurs when two materials from different positions on the galvanic scale come into contact with each other in the presence of a conductive liquid. Galvanic corrosion causes one of the materials to corrode or to be gradually eaten away.
Estimated completion time (hours): 0.7
Objectives
By the end of this course, you will be able to do the following:
- Define galvanic corrosion
- Explain the galvanic scale
- Define noble metals
- List methods for preventing galvanic corrosion

Core potting compound is a lightweight paste resin used to fill the edges or other areas of a honeycomb core in a sandwich structure.
Estimated completion time (hours): 0.7
Objectives
By the end of this course, you will be able to do the following:
- Define potting
- Define core potting compound
- Describe why core potting compound is used
- Explain material compatibility of core potting compound
